|
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels are active solar devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They come in a variety of rectangular shapes and are usually installed in combination to produce electricity. Here is an image which will help you better understand some basic terminology. 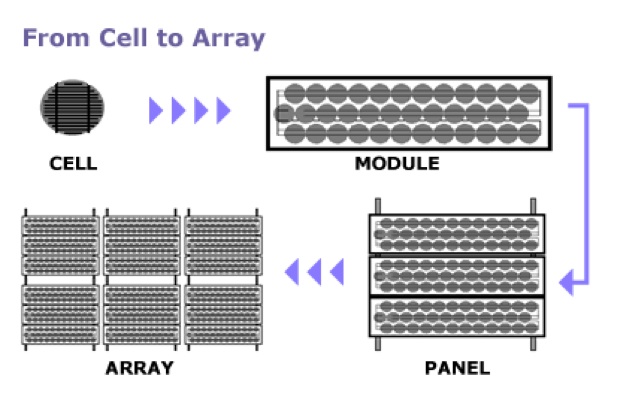
Solar Cell: Semiconductor device that converts sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity Module: PV modules consist of PV cell circuits sealed in an environmentally protective laminate and are the fundamental building block of PV systems Solar Panel: Includes one or more PV modules assembled as a pre-wired, field-installable unit Array: A PV array is the complete power-generating unit, consisting of any number of PV modules and panels
The following is a breakdown (based on installations in the USA) showing where solar panels are used.

The primary component of a solar panel is the solar cells, or photovoltaic cell. This is the key component that converts sunlight into electricity. At the present time about 80% of all solar panels are made from crystalline silicon (i.e., monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous silicon, or hybrids) solar cells. Typically the solar cells are laid out in a grid pattern – with perhaps as many as 72 different solar cells. The other 20% consist primarily of solar cells made mostly from Cadmium Telluride and a small but growing amount from CIGS. The appeal of these types of cells is their low cost resulting from the fact they can be made in large single sheets. There is a lot of research going on in the industry to develop more efficient and lower cost solar panels. Click on Solar Research to learn about some of these developments. The solar panels, after usually after being hermetically sealed to protect them are covered in a non-reflective glass to protect the solar cells from environmental damage and placed into a rigid frame. Typically, the frame is designed to prevent it from deforming due to freezing weather or strong winds. The frame will usually include a drainage hole to help prevent water buildup on the panels, which can reduce output. The back of the panel is also sealed to prevent damage. This is typically where the junction box is located. Tip: Several companies have begun embedding electronics into PV junction boxes. This enables performing Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) for each module individually, and the measurement of performance data for monitoring and fault detection at module level. Some of these solutions make use of Power Optimizers, a DC to DC converter technology developed to maximize the power harvest from solar photovoltaic systems. To learn more read our blog article Back of the Panel Boost for Solar Power.
Typically – solar panels are made in two basic steps – making of the cells, and final module assembly and packing The following video produced by Suntech (the largest producer of crystalline solar panels), that shows how their solar panels are produced:
Each manufacturer is required to provide a datasheet, which you can typically download from the company's website. Using standardized testing protocols (to make comparison between solar panels possible) each manufacturer will list the peak output of the panel (or kWp as it is abbreviated in Europe). Unless the power is needed to charge a battery – an inverter converts the DC electricity to AC electricity that can be used in the home or sold back to the grid.
The amount of power solar panels produce is influenced by the amount of sunlight falling on your specific location per year, the efficiency of the underlying solar cell technology, the materials and technology used in making the solar panel, keeping your panels clean, and the amount of time the solar panel has been in use. When purchasing solar panels, it is therefore wise to look beyond size and look at the dollars/watt ratio. As solar project developers in Europe - we look more at the estimated kWh produced over the life of the solar panel … and calculate what our net return on investment will be. To learn more about the basic factors that affect the amount of power a solar panel will produce – read some of our other posts, namely: Irradiance – how much solar energy reaches the earth Insolation – how much solar energy reaches each spot on the earth Heat – and how this can lower the amount of power produced Cleanliness – and how this can lower the amount of power produced kWh – how to calculate expected solar power production / per year Duration - Solar panels are usually rated for 25 years – but can last much longer, however solar cells become less efficient over time (each type of solar cell technology has a different life span – with monocrystalline cells lasting the longest and the thin-film technologies – being the shortest). Tip: In many cases the solar panels will last longer than the roof – so this is something to consider on a large installation. Tip: Before buying a solar panel – read the performance warranty. These vary by company – and provide you with a good way to see how much confidence the manufacturer has in their own quality control (i.e., better made panels have better performance warranties). When running your calculations to see how much electricity your panels will produce use the amount that is guaranteed (not the listed peak power) – it's a bit more conservative – but a more reliable estimate in the long run. Back from What Are Solar Panels to our Home Page for Solar Energy
|


