Vitamin D from the Sun: Here's What you Need to Know
One of the best benefits from our stars is that your body is designed to produce vitamin D from the sun.
But it's not as easy as it sounds. It's ironic, but there is actually a lot more information available about producing electricity from the sun using PV panels, then there is about producing vitamin D from the sun.
Sure – electricity from the sun is great for you pocketbook. But vitamin D is great for your health – and your whole life.
That's why I've collected a lot of information in this section about how to produce vitamin D from the sun … and what you understand how you do this and to make sure you do so safely.
How the Skin Produces Vitamin D
First – let's look at some basic information. The skin consists of two primary layers: the inner layer called the dermis, composed largely of connective tissue, and the outer, thinner epidermis. Here's a drawing I found in Wikipedia that shows the five different layers of the epidermis.
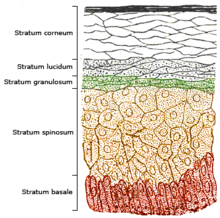
Production of vitamin d from the sun is greatest in the stratum basale (colored red in the illustration) and stratum spinosum (colored light brown).
Vitamin D3 is made in the skin when 7-dehydrocholesterol absorbs UVB ultraviolet light at wavelengths between 270–300 nm, with peak synthesis occurring between 295-297 nm.
Note: The skin has an enormous capacity for vitamin D production and supplies the body with 80-100% of its requirements of vitamin D (subject to sufficient UVB radiation and time of exposure).
Don't Be Afraid To Go Outside
You’ve been told to avoid sunshine … keep indoors during peak sun hours … cover yourself with sunscreen if you go outside … wear long-sleeved shirts and sunglasses even when it’s not sunny… and limit your direct contact with the sun’s rays to zero.
Dermatologists tell us that the sun causes skin cancer. But what they don't tell you -- is that the vitamin D from the sun you get evidence helps you prevent 17 different kinds of cancer.
But our fear of skin cancer keeps us slathered with sunscreen. And that’s bad new. It now turns out, that since the invention of sunscreens - deadly melanoma cancers have increased -- and new research shows that a lack Vitamin D can trigger deadly cancers, depression, bone loss, heart disease and more.
Getting vitamin D from the sun is essential for making a critical vitamin and hormone that protects you from disease and carries out thousands of major functions in your body every day.
Besides being good for your body - it's great for your spirit. Have you ever noticed how you feel happier sitting or walking in the sun? Doesn’t just going outside in the sun calm your nerves and lift your spirits?
There’s a reason for this. Your body needs sunlight in the same way it needs nutrients. In addition to the noticeable lift it gives your mood, it also helps lower your blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar, improve your immunity, regulate your weight, reverse many chronic diseases, protect you from many cancers and improve your overall health and happiness.
So don't be afraid ... enjoy that sunshine. It's good for you.
And don't let the chemical companies prevent you.
Some Factors That Affect Vitamin D Production
Just as there are factors, which affect how much electricity you can produce from PV panels – there are a number of factors, which will affect how effective your body will produce vitamin D from the sun.
Here are a list of some of some of the factors to keep in mind.
1) Amount of skin: Think of a 5 sq. cm patch of your skin like a solar cell. The more skin you expose – the more vitamin D your body will produce. The corollary implication is that if you are only exposing your face, neck and arms – the longer you are going to need to stay in the sun.
2) UVB radiation: Your skin requires UVB radiation to produce vitamin D. Since glass blocks UVB – this means you need to be outdoors in the sun. As we discussed in our section on irradiance, UVB is produced by the sun; and in our section on insolation, the amount of the sun's radiation varies with latitude, altitude (e.g. in Denver you need 20% less time in the sun because of the altitude), weather conditions, time of day, time of year, etc.
While it is generally true that you can produce solar energy – as long as there is visible sunlight, the research on producing vitamin D from the sun seems to suggest that there is a threshold level of UVB your skin requires in order to produce Vitamin D.
In other words – depending on where you live - the number of days and hours where there is sufficient UVB radiation your sun can use to produce Vitamin D will vary. So while it might take you 15 minutes in the peak (10:00 AM to 2:00 PM) time in the summer to produce the vitamin D you need – it could take much longer than that in the spring and fall (substantially more if the weather is still chilly and you are wearing more clothing), and may not be possible at all in the winter.
Note: In a recent blog post, I reported on some interesting observations about in increase in visible light energy while at the same time there has been a drop off in UV radiation produced by the sun. For more about this subject click here.
3) Sunscreen: If you use sunblock with a SPF rating of 8 or higher, it can block up to 95% of the UVB rays reaching your skin – meaning you can't produce vitamin D from the sun if you use a sun screen.
4) Age: As you age, your skin gets thinner, and less efficient in producing vitamin D from the sun. Up to age 20 you might need 15 minutes of peak period sun, by age 64 you probably will need to stay in the sun twice as long.
5) Air Pollution: While UV radiation can penetrate clouds, air pollution can reduce how much UVB energy you receive. So if you work in the city and want to get some sun on your lunch break – you might need to spend more time outside – then you might in the suburbs where the pollution levels are more likely to be lower.
6) BMI: Although I don't have hard numbers, I've read that the greater your BMI, the less efficient your body will be in producing vitamin D from the sun. Interestingly, there is some research that suggests that keeping your vitamin D levels near optimum levels can help you reduce weight – although exactly how it does this is not fully understood at this time.
7) Diet: There is some evidence to suggest that adherence to strict vegetarianism can reduce your efficiency in producing vitamin D from the sun.
8) Presciptions: Certain drugs, anti-biotics or corticosteroids can reduce your efficiency / prevent your body from producing vitamin D from the sun.
9) Pigmentation: It's difficult to quantify how much since skin pigmentation affects how much radiation your skin absorbs: The darker the skin, the more it's protected against skin cancer but the less able it is to absorb UV-B rays.
It also depends on how much skin is exposed and the time of day. If you're fair skinned and sunning yourself outside in a bathing suit at noon, you only need a few minutes without sunscreen.
Generally, as your skin gets more and more color you need more time to produce vitamin D from the sun. For example, some studies have indicated that someone with black skin may require six times the sun exposure to make the same vitamin D levels as a very fair-skinned un-tanned person.
Note: As you tan, you need more and more time in the sun to produce vitamin D from the sun, because the darker your skin, the less efficient it is in producing Vitamin D.
Proper Exposure Amounts
It would be nice if there could be
guidelines established giving people an idea as to what the right
exposure levels would be given different variables including time of the
year, time of the day, location and amount of clothing worn.
Obviously
someone taking a lunch break walking in the park is not going to get as
much exposure wearing slacks and a short sleeved shirt as someone would
laying by the pool wearing a bathing suit or less.
According to
Dr. Michael Holick, from Boston University, limited sun exposure of 5-10
minutes three times a week, during the spring, summer and fall, during
the mid-day from 11am to 2pm, on the face and arms, will provide enough
vitamin D for the individual. This sun exposure will also allow for
storage of some of the excess vitamin D during the winter, when the UVB
rays will not reach some areas.
This amount is also recommended
by the Linus Pauling Institute, which also advises healthy adults to
take a daily multivitamin supplement containing vitamin D.
Advice:
If you can – get out of the building for lunch, take a walk and get
some sun. It's one of the best things you can do for yourself.
Also
– if you're starting to get the winter blues – consider taking a trip
to a sunny place closer to the equator where you can enjoy yourself while you get your vitamin D from the sun - just be cautious.
Automatic Shut-off
One
of the cool things about our bodies – is that you never have to worry
about producing too much vitamin D. Once your body gets enough, it
will basically stop producing any more.
Unfortunately, we never
know when this happens – and so there is the risk that by staying out
longer – you could expose yourself to a greater risk to cancer. On the
other hand, the more vitamin D you have in your body – the more
resistant you are to getting cancer. A bit of a catch 22.
As always, use your common sense and listen to your body.
Protecting Your Skin Naturally
If you plan to spend more than 20 minutes of fun in the sun, there are natural ways to protect yourself. Here are some tips.
Get enough antioxidants, one of your best lines of defense against all types of skin damage.
Vitamin
D3: Take 5,000 to 10,000 IUs per day (I take 2 5,000 iu Vit D3 gel caps daily), particularly during the winter or if you live in
cold, damp climates with little sunlight.
Advice:
Vitamin C. Fights free radicals, reduces inflammation, and boosts immune response. Take 500 mg twice per day with food.
Vitamin E. Great for skin health. I recommend 400 IU per day. Look for vitamin E as “mixed tocopherols” on the label. They are the organic compounds most readily absorbed by your body.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid. A powerful antioxidant that protects skin cells from free radicals, guards their mitochondria (the power plant of every cell), and pumps up your cancer defense mechanisms. I recommend 200 mg to 400 mg daily.
Get enough omega-3s. Studies show that omega 6:3 ratio is important in preventing skin cancer.
You might also want to try rubbing a little mango butter or shea butter on your skin as a sun blocker without the toxic chemicals. You can also use zinc oxide, a natural mineral that provides a reflective barrier on your skin. You can find these in most health food and supplement stores.
Sunburn & Vitamin D
As
I was preparing this web page – I ran across some interesting anecdotal
evidence that suggests that if you are a fair-skinned person and burn
easily, you can reduce your risk of sunburn by taking vitamin D
supplements before going out in the sun (i.e., that first time going to
the beach after being mostly indoors all winter).
Should I Take Supplements?
Take stock of your living situation. If the sun is available regularly where you live, go that route whenever possible. It’s free, it’s safe, it’s easy, and it’s enjoyable. Avoid burning, ease on into it, you’ll be safe.
Remember, you in the beginning of each "sunny seaon", be careful. Five minutes of unfiltered rays can turn a freckled redhead lobster-pink, sore, and resigned to indoor living. Ease into things. Learn your limits, and throw on a shirt or find some shade before you burn.
However, most people's schedules will allow only a few days of sunbathin a year then you'll probably want to consider taking a Vit D supplement.
There are a number of different opinions regarding how much you should take. Personally, since our body typically produces 10,000 IU of Vit D3 - I figure that's a good amount to take.
If you are outside of the USA - or want to take larger doses - you'll probably have to shop online.
Learn More About the Sunshine Vitamin
It takes more than a good internet connection to fully understand how the body reacts to the sun, specifically how it pulls vitamins from the star's rays. Sure, one can go to college and spend years away from home studying. But if you find yourself with responsibilities keeping you in one area and can't make the physical hike, you can pursue online BSN nursing programs without leaving the comfort of your home
Some Related Articles You Might Find Interesting
Vitamin D is important for good health and long-life and since your body is designed to produce vitamin D from the sun - we think it is one of the best benefits you can get from the sun.
But just like solar energy - there is a lot more to learn about how vitamin D helps you be healthy - and can really mess you up when you don't get out in the sun enough.
Here are some of the articles we've added to our website to give you a full picture of this important subject. Like other parts of this website these articles summarize the important facts and include useful advice.
If Vitamin D Were a Drug It Would Win the Nobel
Prize
Benefits of Vitamin D
Vitamin D Deficiency: Symptoms and Risk
Factors
Testing Your Vitamin D Levels: (know what to ask
your doctor, or order a home testing kit)
Vitamin D from Food
What you need to know when choosing a Vitamin D
supplement
Vitamin D Deficiency is linked to 2/3rds of the
medical problems in the US along with poor diet
Vitamin D helps prevent 75% of all cancers
Vitamin D is Important for Good Heart
Health
Vitamin D and Calcium: You Need Them Both
Vitamin D is important for healthy teeth and
preventing periodontal disease and weakening of the jawbone
Vitamin D deficiency can cause mobility
problems
Vitamin D helps you live longer
Get More Solar Facts and Advice
To learn more facts and advice about a wide variety of solar related products and issues - use our built-in site & blog searching tool below. We have written more than 700 articles to help you.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this section of our web site is for educational purposes and is not intended as medical advice.
While
the publishers of this website believe that people have the right to
understand their own bodies and to take care of their bodies as they see
fit, we also respect the knowledge and experience of trained
nutritionists, scientists, researchers, medical practioners, and others
who can help you achieve the optimum health you are entitled to, and
suggest you seek out and work with health specialists you can trust.